The media attribute specifies what media or device the linked document is optimized for. This attribute is used to specify that the target URL is designed for special devices (like iPhone), speech or print media. This attribute can accept several values. Only used if the href attribute is present.
The @media rule is used in media queries to apply different styles for different media types/devices.
Media queries can be used to check many things, such as:
- width and height of the viewport
- width and height of the device
- orientation (is the tablet/phone in landscape or portrait mode?)
- resolution
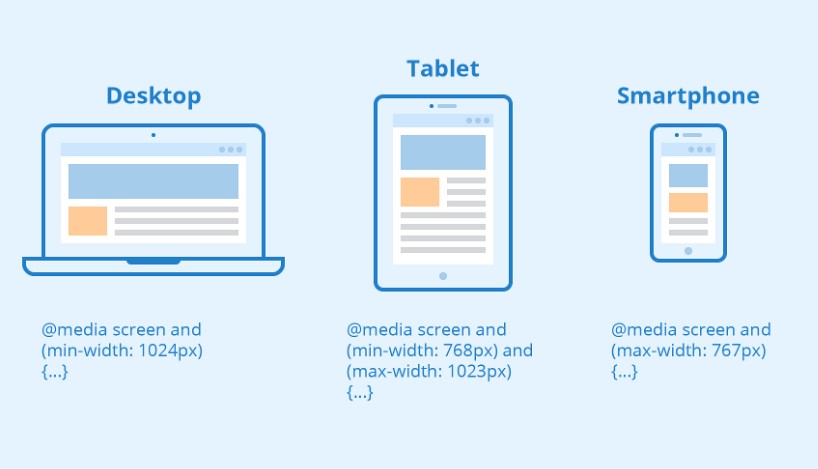
Using media queries are a popular technique for delivering a tailored style sheet (responsive web design) to desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile phones.
You can also use media queries to specify that certain styles are only for printed documents or for screen readers (mediatype: print, screen, or speech).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>
<style>
.example {
padding: 20px;
color: white;
}
/* Extra small devices (phones, 600px and down) */
@media only screen and (max-width: 600px) {
.example {background: red;}
}
/* Small devices (portrait tablets and large phones, 600px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 600px) {
.example {background: green;}
}
/* Medium devices (landscape tablets, 768px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) {
.example {background: blue;}
}
/* Large devices (laptops/desktops, 992px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 992px) {
.example {background: orange;}
}
/* Extra large devices (large laptops and desktops, 1200px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 1200px) {
.example {background: pink;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Typical Media Query Breakpoints</h2>
<p class=”example”>Resize the browser window to see how the background color of this paragraph changes on different screen sizes.</p>
</body>
</html>
You can also have different stylesheets for different media, like this: See All Example
| @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { .topnav a { float: none; width: 100%; } } |
| body { background-color: lightblue; }@media screen and (min-width: 400px) { body { background-color: lightgreen; } }@media screen and (min-width: 800px) { body { background-color: lavender; } } |
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
div.example {
display: none;
}
}
<link rel=”stylesheet” media=”screen and (min-width: 900px)” href=”widescreen.css”>
<link rel=”stylesheet” media=”screen and (max-width: 600px)” href=”smallscreen.css”>
/* On screens that are 992px wide or less, go from four columns to two columns */
@media screen and (max-width: 992px) {
.column {
width: 50%;
}
}/* On screens that are 600px wide or less, make the columns stack on top of each other instead of next to each other */
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
.column {
width: 100%;
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head>
<title>Media Query</title><style>/* Media Query for Mobile Devices */
@media (max-width: 480px) {
body {
background-color: red;
}
}/* Media Query for low resolution Tablets, Ipads */
@media (min-width: 481px) and (max-width: 767px) {
body {
background-color: yellow;
}
}/* Media Query for Tablets Ipads portrait mode */
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1024px){
body {
background-color: blue;
}
}
/* Media Query for Laptops and Desktops */
@media (min-width: 1025px) and (max-width: 1280px){
body {
background-color: green;
}
}
/* Media Query for Large screens */
@media (min-width: 1281px) {
body {
background-color: white;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body style = “text-align:center;”>
<h1>CODING FOR BEGINNERS</h1>
<h2>Media Query</h2>
</body>
</html>
/* At the top level of your code */
@media screen and (min-width: 900px) {
article {
padding: 1rem 3rem;
}
}/* Nested within another conditional at-rule */
@supports (display: flex) {
@media screen and (min-width: 900px) {
article {
display: flex;
}
}
}
Media Types
Value
Description
all
Default. Used for all media type devices
print
Used for printers
screen
Used for computer screens, tablets, smart-phones etc.
speech
Used for screenreaders that “reads” the page out loud
Media Features
Value
Description
any-hover
Does any available input mechanism allow the user to hover over elements? (added in Media Queries Level 4)
any-pointer
Is any available input mechanism a pointing device, and if so, how accurate is it? (added in Media Queries Level 4)
aspect-ratio
The ratio between the width and the height of the viewport
color
The number of bits per color component for the output device
color-gamut
The approximate range of colors that are supported by the user agent and output device (added in Media Queries Level 4)
color-index
The number of colors the device can display
grid
Whether the device is a grid or bitmap
height
The viewport height
hover
Does the primary input mechanism allow the user to hover over elements? (added in Media Queries Level 4)
inverted-colors
Is the browser or underlying OS inverting colors? (added in Media Queries Level 4)
light-level
Current ambient light level (added in Media Queries Level 4)
max-aspect-ratio
The maximum ratio between the width and the height of the display area
max-color
The maximum number of bits per color component for the output device
max-color-index
The maximum number of colors the device can display
max-height
The maximum height of the display area, such as a browser window
max-monochrome
The maximum number of bits per “color” on a monochrome (greyscale) device
max-resolution
The maximum resolution of the device, using dpi or dpcm
max-width
The maximum width of the display area, such as a browser window
min-aspect-ratio
The minimum ratio between the width and the height of the display area
min-color
The minimum number of bits per color component for the output device
min-color-index
The minimum number of colors the device can display
min-height
The minimum height of the display area, such as a browser window
min-monochrome
The minimum number of bits per “color” on a monochrome (greyscale) device
min-resolution
The minimum resolution of the device, using dpi or dpcm
min-width
The minimum width of the display area, such as a browser window
monochrome
The number of bits per “color” on a monochrome (greyscale) device
orientation
The orientation of the viewport (landscape or portrait mode)
overflow-block
How does the output device handle content that overflows the viewport along the block axis (added in Media Queries Level 4)
overflow-inline
Can content that overflows the viewport along the inline axis be scrolled (added in Media Queries Level 4)
pointer
Is the primary input mechanism a pointing device, and if so, how accurate is it? (added in Media Queries Level 4)
resolution
The resolution of the output device, using dpi or dpcm
scan
The scanning process of the output device
scripting
Is scripting (e.g. JavaScript) available? (added in Media Queries Level 4)
update
How quickly can the output device modify the appearance of the content (added in Media Queries Level 4)
width
The viewport width